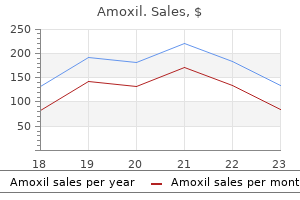
| Product name | Per Pill | Savings | Per Pack | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 pills | $3.22 | $32.16 | ADD TO CART | |
| 20 pills | $2.59 | $12.57 | $64.32 $51.75 | ADD TO CART |
| 30 pills | $2.38 | $25.14 | $96.48 $71.34 | ADD TO CART |
| 60 pills | $2.17 | $62.85 | $192.96 $130.11 | ADD TO CART |
| 90 pills | $2.10 | $100.56 | $289.44 $188.88 | ADD TO CART |
| 120 pills | $2.06 | $138.27 | $385.92 $247.65 | ADD TO CART |
| 180 pills | $2.03 | $213.69 | $578.88 $365.19 | ADD TO CART |
| 270 pills | $2.01 | $326.82 | $868.32 $541.50 | ADD TO CART |
| 360 pills | $1.99 | $439.95 | $1157.76 $717.81 | ADD TO CART |
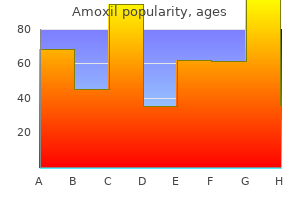
| Product name | Per Pill | Savings | Per Pack | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 pills | $1.48 | $29.60 | ADD TO CART | |
| 30 pills | $1.28 | $5.95 | $44.40 $38.45 | ADD TO CART |
| 60 pills | $1.08 | $23.82 | $88.80 $64.98 | ADD TO CART |
| 90 pills | $1.02 | $41.68 | $133.20 $91.52 | ADD TO CART |
| 120 pills | $0.98 | $59.55 | $177.60 $118.05 | ADD TO CART |
| 180 pills | $0.95 | $95.28 | $266.40 $171.12 | ADD TO CART |
| 270 pills | $0.93 | $148.87 | $399.60 $250.73 | ADD TO CART |
| 360 pills | $0.92 | $202.46 | $532.80 $330.34 | ADD TO CART |
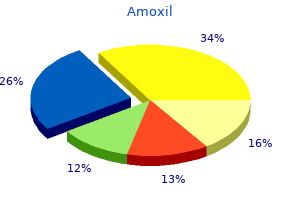
| Product name | Per Pill | Savings | Per Pack | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 pills | $0.80 | $24.12 | ADD TO CART | |
| 60 pills | $0.57 | $13.95 | $48.24 $34.29 | ADD TO CART |
| 90 pills | $0.49 | $27.89 | $72.36 $44.47 | ADD TO CART |
| 180 pills | $0.42 | $69.73 | $144.72 $74.99 | ADD TO CART |
| 240 pills | $0.40 | $97.62 | $192.96 $95.34 | ADD TO CART |
| 360 pills | $0.38 | $153.40 | $289.44 $136.04 | ADD TO CART |
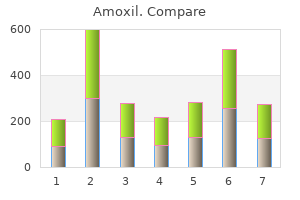
| Product name | Per Pill | Savings | Per Pack | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 pills | $0.45 | $27.04 | ADD TO CART | |
| 90 pills | $0.40 | $4.87 | $40.56 $35.69 | ADD TO CART |
| 120 pills | $0.37 | $9.73 | $54.07 $44.34 | ADD TO CART |
| 180 pills | $0.34 | $19.47 | $81.11 $61.64 | ADD TO CART |
| 270 pills | $0.32 | $34.07 | $121.67 $87.60 | ADD TO CART |
| 360 pills | $0.32 | $48.67 | $162.22 $113.55 | ADD TO CART |
"250 mg amoxil purchase with amex, antibiotic resistance database".
Y. Peratur, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Campbell University School of Osteopathic Medicine
Some more recently developed cephalosporins are resistant to the destructive beta-lactamase enzyme produced by many bacteria 5 infection control measures discount amoxil 500 mg buy. Ciprofloxacin: A broad-spectum fluoroquinolone antibiotic that is important in treating serious bacterial infections virus international buy cheap amoxil 250 mg on line, especially when resistance to older antibiotic classes is suspected virus 2 discount 500 mg amoxil with visa. Clindamycin: An antibiotic used to treat certain types of bacterial infections, including infections of the lungs, skin, blood, female reproductive organs, and internal organs. Conjugate vaccine: A vaccine in which an antigen is attached to a carrier protein from the same microorganism. This approach enhances the immunological response to the vaccine and thereby enhances the overall effectiveness of the vaccine. Epidemiology: The study of diseases to find out who is affected, how disease is spread, trends in illnesses and deaths, what behaviors or other risk factors might put a person at risk, and other information that can be used to develop prevention strategies. Epidemiologists use surveys and surveillance systems to track illnesses, and they often investigate disease outbreaks. Erythromycin: An antibiotic used to treat certain infections caused by bacteria, such as bronchitis, diphtheria, Legionnaires’ disease, pertussis (whooping cough), pneumonia, rheumatic fever, sexually transmitted diseases, and infections of the ear, intestine, lung, urinary tract, and skin. Extended-spectrum antibiotic: An antibiotic that has been chemically modified to attack additional types of bacteria, usually those that are gram-negative. Fluoroquinolones: Broad-spectrum antibiotics that play an important role in treatment of serious bacterial infections, especially hospital-acquired infections and others in which resistance to older antibacterial classes is suspected. Fungi can also be or pathogens (such as the endemic mycoses, histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis, and superficial mycoses) that cause infections in healthy people. Fungi are used to develop antibiotics, antitoxins, and other drugs used to treat various diseases. Hypervirulent: Increased ability to cause severe disease, relapse rates, and death. Isolate/bacterial isolate: A pure culture or sample of bacteria used to study their properties. Macrolide: A type of antibiotic used to treat infections caused by gram-positive bacteria and infections such as respiratory tract and soft-tissue infections. Macrolides are often used in people allergic to penicillin, but resistance to macrolides is increasing and has made them less useful. Morbidity: The number of people who are infected with a specified illness in a given time period. The exact number of drugs that a microorganism is resistant to varies depending on the infection or pathogen. Narrow-spectrum antibiotic: An antibiotic that is active against a limited range of bacteria. Outbreak: When a group of people develop the same illness around the same time, and the number of people affected is higher than normal. Outbreak investigations are conducted to identify what exposure the affected people had in common. Penicillins: A class of antibiotics including amoxicillin, methicillin, piperacillin and other drugs based on the first true antibiotic discovered in 1928 by Dr. Pneumonia: An inflammatory condition of the lungs affecting primarily the microscopic air sacs known as alveoli. It is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and typical symptoms include a cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. Reservoir: A person, animal, insect, plant, or other host that is carrying a pathogen (for example, bacteria or fungi) that causes infectious diseases. Resistant bacteria: Microorganisms that have changed in ways that reduce or eliminate the effectiveness of drugs, chemicals, or other agents to cure or prevent infections. Strain/bacterial strain: A strain is a genetic variant or subtype of a microorganism (for example, a flu strain is a subtype of the flu virus). When bacteria become resistant to antibiotics, they can share their resistance with other bacteria to create new resistant bacterial strains.
If we drink too much coffee or beer is taking antibiotics for acne safe order line amoxil, the caffeine or alcohol influences the activity in our brain antibiotic 3 times a day order generic amoxil, and our consciousness may change human antibiotics for dogs ear infection discount amoxil 250 mg with mastercard. When we are anesthetized before an operation or experience a concussion after a knock on the head, we may lose consciousness entirely as a result of changes in brain activity. We also lose consciousness when we sleep, and it is with this altered state of consciousness that we begin our chapter. Draw a graphic showing the usual phases of sleep during a normal night and notate the characteristics of each phase. Outline and explain the similarities and differences among the different theories of dreaming. The lives of all organisms, including humans, are influenced by regularly occurring cycles of behaviors known as biological rhythms. One important biological rhythm is the annual cycle that guides the migration of birds and the hibernation of bears. Women also experience a 28-day cycle that guides their fertility and menstruation. But perhaps the strongest and most important biorhythm is the daily circadian rhythm (from the Latin circa, meaning “about‖ or “approximately,‖ and dian, meaning “daily‖) that guides the daily waking and sleeping cycle in many animals. Many biological rhythms are coordinated by changes in the level and duration of ambient light, for instance, as winter turns into summer and as night turns into day. In some animals, such as birds, the pineal gland in the brain is directly sensitive to light and its activation influences behavior, such as mating and annual migrations. The ganglion cells in the retina send signals to a brain area above the thalamus called the suprachiasmatic nucleus, which is the body’s primary circadian “pacemaker. In response, the pineal gland secretes melatonin, a powerful hormone that facilitates the onset of sleep. Research Focus: Circadian Rhythms Influence the Use of Stereotypes in Social Judgments The circadian rhythm influences our energy levels such that we have more energy at some times of day than others. To test this hypothesis, he asked 189 research participants to consider cases of alleged misbehavior by other college students and to judge the probability of the accused students‘ guilt. The accused students were identified as members of particular social groups, and they were accused of committing offenses that were consistent with stereotypes of these groups. One case involved a student athlete accused of cheating on an exam, one case involved a Hispanic student who allegedly physically attacked his roommate, and a third case involved an African American student who had been accused of selling illegal drugs. Each of these offenses had been judged via pretesting in the same student population to be stereotypically (although, of course, unfairly) associated with each social group. The research participants were also provided with some specific evidence about the case that made it ambiguous whether the person had actually committed the crime, and then asked to indicate the likelihood of the student‘s guilt on an 11-point scale (0 = extremely unlikely to 10 = extremely likely). Participants also completed a measure designed to assess their circadian rhythms—whether they were more active and alert in the morning (Morning types) or in the evening (Evening types). The participants were then tested at experimental sessions held either in the morning (9 a. Morning people used their stereotypes more when they were tested in the evening, and evening people used their stereotypes more when they were tested in the morning. Sleep researchers have found that sleeping people undergo a fairly consistent pattern of sleep stages, each lasting about 90 minutes. During this sleep stage our muscles shut down, and this is probably a good thing as it protects us from hurting ourselves or trying to act out the scenes that are playing in our dreams. Each of the sleep stages has its own distinct pattern of brain [4] activity (Dement & Kleitman, 1957). When we are awake, our brain activity is characterized by the presence of very fast beta waves. When we first begin to fall asleep, the waves get longer (alpha waves), and as we move into stage N1 sleep, which is characterized by the experience of drowsiness, the brain begins to produce even slower theta waves. During stage N1 sleep, some muscle tone is lost, as well as most awareness of the environment.
Skinner studied antibiotics for ear infections amoxil 250 mg buy mastercard, in detail infection kidney generic 500 mg amoxil free shipping, how animals changed their behavior through reinforcement and punishment antibiotic for kidney infection buy generic amoxil 250 mg line, and he developed terms that explained the processes of operant learning (Table 7. Skinner used the termreinforcer to refer to any event that strengthens or increases the likelihood of a behavior and the term punisher to refer to any event that weakens or decreases the likelihood of a behavior. And he used the terms positive and negative to refer to whether a reinforcement was presented or removed, respectively. Thus positive reinforcement strengthens a response by presenting something pleasant after the response and negative reinforcement strengthens a response by reducing or removing something unpleasant. For example, giving a child praise for completing his homework represents positive reinforcement, whereas taking aspirin to reduced the pain of a headache represents negative reinforcement. In both cases, the reinforcement makes it more likely that behavior will occur again in the future. Punishment, on the other hand, refers to any event that weakens or reduces the likelihood of a behavior. Positive punishment weakens a response by presenting something unpleasant after the response, whereasnegative punishment weakens a response by reducing or removing something pleasant. A child who is grounded after fighting with a sibling (positive punishment) or who loses out on the opportunity to go to recess after getting a poor grade (negative punishment) is less likely to repeat these behaviors. Although the distinction between reinforcement (which increases behavior) and punishment (which decreases it) is usually clear, in some cases it is difficult to determine whether a reinforcer is positive or negative. On a hot day a cool breeze could be seen as a positive reinforcer (because it brings in cool air) or a negative reinforcer (because it removes hot air). One may smoke a cigarette both because it brings pleasure (positive reinforcement) and because it eliminates the craving for nicotine (negative reinforcement). It is also important to note that reinforcement and punishment are not simply opposites. The use of positive reinforcement in changing behavior is almost always more effective than using punishment. This is because positive reinforcement makes the person or animal feel better, helping create a positive relationship with the person providing the reinforcement. Types of positive reinforcement that are effective in everyday life include verbal praise or approval, the awarding of status or prestige, and direct financial payment. Punishment, on the other hand, is more likely to create only temporary changes in behavior because it is based on coercion and typically creates a negative and adversarial relationship with the person providing the reinforcement. When the person who provides the punishment leaves the situation, the unwanted behavior is likely to return. The trainer gave a command and the dolphin swam to the bottom of the pool, picked up a ring on its nose, jumped out of the water through a hoop in the air, dived again to the bottom of the pool, picked up another ring, and then took both of the rings to the trainer at the edge of the pool. The animal was trained to do the trick, and the principles of operant conditioning were used to train it. But these complex behaviors are a far cry from the simple stimulus-response relationships that we have considered thus far. One way to expand the use of operant learning is to modify the schedule on which the reinforcement is applied. To this point we have only discussed a continuous reinforcement schedule, in which the desired response is reinforced every time it occurs; whenever the dog rolls over, for instance, it gets a biscuit. Continuous reinforcement results in relatively fast learning but also rapid extinction of the desired behavior once the reinforcer disappears. The problem is that because the organism is used to receiving the reinforcement after every behavior, the responder may give up quickly when it doesn‘t appear. Most real-world reinforcers are not continuous; they occur on a partial (or intermittent) reinforcement schedule—a schedule in which the responses are sometimes reinforced, and sometimes not. In comparison to continuous reinforcement, partial reinforcement schedules lead to slower initial learning, but they also lead to greater resistance to extinction. Because the reinforcement does not appear after every behavior, it takes longer for the learner to determine that the reward is no longer coming, and thus extinction is slower. In a fixed-interval schedule, reinforcement occurs for the first response made after a specific amount of time has passed. For instance, on a one-minute fixed-interval schedule the animal receives a reinforcement every minute, assuming it engages in the behavior at least once during the minute. An example might be checking your e-mail: You are reinforced by receiving messages that come, on average, say every 30 minutes, but the reinforcement occurs only at random times. Interval reinforcement schedules tend to produce slow and steady rates of responding.
Syndromes
Ernestine Wiedenbach antibiotics just in case discount 500 mg amoxil, Virginia Henderson virus y antivirus cheap amoxil express, and Ernestine Wiedenbach died in April 1998 at the age Ida Jean Orlando are three of the most important of 98 (Gesse & Dombro 7dtd infection amoxil 250 mg purchase overnight delivery, 1992, p. The work of each of these nurse scholars was based on Ida Jean Orlando was born in 1926 in New York. Concepts College School of Nursing where she received a and terms they first used are heard today around diploma in nursing. John’s University in Brooklyn, New York, and these three important twentieth-century nursing in 1954 she completed a master’s degree in nurs- theorists. Orlando’s early work from scholars who have studied or worked nursing practice experience included obstetrics, with these theorists and who wrote chapters about medicine, and emergency room nursing. Her first each for Nursing Theories and Nursing Practice 1st book, The Dynamic Nurse-Patient Relationship: edition. To the extent possible, content written by Function, Process and Principles (1961), was based each of the identified authors is used. For a wealth on her research and blended nursing practice, of additional information on these nurses, scholars, psychiatric–mental health nursing, and nursing ed- researchers, thinkers, writers, practitioners, and ed- ucation. It was published when she was director ucators, please consult the reference and bibliogra- of the graduate program in mental health and phy sections at the end of this chapter. She received a bachelor of arts degree from tative and inductive, using naturalistic inquiry Wellesley College in 1922. As a consultant at McLean Hospital in Johns Hopkins School of Nursing in 1925 (Nickel, Belmont, Massachusetts, Orlando continued to Gesse, & MacLaren, 1992. After completing a study nursing practice and developed a training master of arts at Columbia Univeristy in 1934, she program and nursing service department based on became a professional writer for the American her theory. With two opment of prescriptive theory (Dickoff, James & of her brothers serving in the armed forces during Wiedenbach, 1968). Even after her retirement in World War I and in anticipation of a critical short- 1966, she and her lifelong friend Caroline Falls of- age of nurses, Virginia Henderson entered the Army fered informal seminars in Miami, always remind- School of Nursing at Walter Reed Army Hospital. It ing students and faculty of the need for clarity of was there that she began to question the regimen- purpose, based on reality. She even continued to talization of patient care and the concept of nurs- use her gift for writing to transcribe books for the ing as ancillary to medicine (Henderson, 1991). Her pioneer work in the area of “series of almost unrelated procedures, beginning identifying and structuring nursing knowledge has with an unoccupied bed and progressing to aspira- provided the foundation for nursing scholarship tion of body cavities” (Henderson, 1991, p. Henderson admired Goodrich’s intel- Introducing the Theories lectual abilities and stated: “Whenever she visited our unit, she lifted our sights above techniques Virginia Henderson, sometimes known as the and routine” (Henderson, 1991, p. Henderson modern day Florence Nightingale, developed the credited Goodrich with inspiring her with the definition of nursing that is most well known inter- “ethical significance of nursing” (Henderson, 1991, nationally. Ida Jean Orlando was perhaps the ence forever influenced her ethical understanding first nurse to use qualitative research methods and of nursing and her appreciation of the importance was the first to articulate nursing concepts based on and complexity of the nurse-patient relationship. Each of these She continued to explore the nature of nursing nurses helped us focus on the patient, instead of on as her student experiences exposed her to different the tasks to be done, and to plan care to meet needs ways of being in relationship with patients and of the person. For instance, a pediatric experience caring based on the perspective of the individual as a student at Boston Floating Hospital introduced being cared for—through observing, communicat- Henderson to patient-centered care in which ing, designing, and reporting. Each was concerned nurses were assigned to patients instead of tasks, with the unique aspects of nursing practice and and warm nurse-patient relationships were encour- scholoarship and with the essential question of, aged (Henderson, 1991). She enjoyed the less formal vis- Initial work on Wiedenbach’s prescriptive theory is iting nurse approach to patient care and became presented in her article in the American Journal skeptical of the ability of hospital regimes to alter of Nursing (1963) and her book, Meeting the patients’ unhealthy ways of living upon returning Realities in Clinical Teaching (1969). She entered Teachers tion of prescriptive theory is that:“Account must be College at Columbia University, earning her bac- calaureate degree in 1932 and her master’s degree “Account must be taken of the motivating in 1934. She continued at Teachers College as an in- factors that influence the nurse not only in structor and associate professor of nursing for the doing what she does but also in doing it next 20 years. Henderson wrote about nursing the way she lived it: focusing on what taken of the motivating factors that influence the nurses do, how nurses function, and on nursing’s nurse not only in doing what she does but also in unique role in health care. Her works are beauti- doing it the way she does it with the realities that fully written in jargon-free, everyday language. The nurse’s central purpose in nursing is the • The Recipient, or the patient receiving this nurse’s professional commitment. For Wiedenbach, action or on whose behalf the action is the central purpose in nursing is to motivate the taken; individual and/or facilitate his efforts to over- • The Framework, comprised of situational fac- come the obstacles that may interfere with his tors that affect the nurse’s ability to achieve ability to respond capably to the demands made nursing results; of him by the realities in his situation • The Goal, or the end to be attained through (Wiedenbach, 1970, p. She emphasized that nursing activity on behalf of the patient; the nurse’s goals are grounded in the nurse’s • The Means, the actions and devices through philosophy, that “those beliefs and values that which the nurse is enabled to reach the shape her attitude toward life, toward fellow goal. She rec- in whatever setting they are found for the purpose of ognized that nurses have different values and avoiding, relieving, diminishing or curing the indi- various commitments to nursing and that to vidual’s sense of helplessness.
Drug and surgical interventions are stopped if they are found to be either ineffective or to have negative consequences bacteria organelle discount amoxil 500 mg. However antibiotics for cat acne purchase amoxil with visa, behavioural interventions to promote behaviour change infections of the eye buy amoxil 500 mg with amex, such as smoking cessation, exercise and weight loss programmes, are developed and promoted even when the evidence for their success is poor. Within health psychology, behavioural programmes are considered neutral enough to be better than nothing. However, obesity treatment using dieting is an example of the potential negative side effects of encouraging individual responsibility for health and attempting to change behaviour. Perhaps behavioural interventions can have as many negative consequences as other medical treatments. Theories are considered either physio- logical or psychological and treatment perspectives are divided in a similar fashion, therefore maintaining a dualistic model of individuals. This paper discusses the recent emphasis on patient responsibility for health and suggests that encouraging the obese to diet may be an example of attempting to control the uncontrollable. This book provides an account of the continuum of eating behaviour from healthy eating, through dieting and body dissatisfaction, obesity and eating disorders. In addition, it describes the ways in which quality of life has been used in research both in terms of the factors that predict quality of life (quality of life as an outcome variable) and the association between quality of life and longevity (quality of life as a predictor). The question asked is, ‘Has the number of people who have died this year gone up, gone down or stayed the same? The next most basic form of mortality rate therefore includes a denominator reflecting the size of the population being studied. Such a measure allows for com- parisons to be made between different populations: more people may die in a given year in London when compared with Bournemouth, but London is simply bigger. In order to provide any meaningful measure of health status, mortality rates are corrected for age (Bournemouth has an older population and therefore we would predict that more people would die each year) and sex (men generally die younger than women and this needs to be taken into account). Furthermore, mortality rates can be produced to be either age specific such as infant mortality rates, or illness specific such as sudden death rates. As long as the population being studied is accurately specified, corrected and specific, mortality rates provide an easily available and simple measure: death is a good reliable outcome. However, the juxtaposition of social scientists to the medical world has challenged this position to raise the now seemingly obvious question, ‘Is health really only the absence of death? However, in line with the emphasis upon simplicity inherent within the focus on mortality rates, many morbidity measures still use methods of counting and recording. For example, the expensive and time-consuming production of morbidity prevalence rates involve large surveys of ‘caseness’ to simply count how many people within a given population suffer from a particular problem. Likewise, sick- ness absence rates simply count days lost due to illness and caseload assessments count the number of people who visit their general practitioner or hospital within a given time frame. However, morbidity is also measured for each individual using measures of functioning. Some of these are referred to simply as subjective health measures, others are referred to as either quality of life scales or health-related quality of life scales. However, the literature in the area of subjective health status and quality of life is plagued by two main questions: ‘What is quality of life? Reports of a Medline search on the term ‘quality of life’ indicate a surge in its use from 40 citations (1966–74), to 1907 citations (1981–85), to 5078 citations (1986–90) (Albrecht 1994). For example, it has been defined as ‘the value assigned to duration of life as modified by the impairments, functional states, perceptions and social opportunities that are influenced by disease, injury, treatment or policy’ (Patrick and Ericson 1993), ‘a personal statement of the positivity or negativity of attributes that characterise one’s life’ (Grant et al. Further, whilst some researchers treat the concepts of quality of life as interchangeable, others argue that they are separate (Bradley 2001). Such problems with definition have resulted in a range of ways of operationalizing quality of life. For example, following the discussions about an acceptable definition of quality of life, the European Organisation for Research on Treatment of Cancer operationalized quality of life in terms of ‘functional status, cancer and treatment specific symptoms, psychological distress, social interaction, financial/economic impact, perceived health status and overall quality of life’ (Aaronson et al. In line with this, their measure consisted of items that reflected these different dimensions. Furthermore, Fallowfield (1990) defined the four main dimensions of quality of life as psychological (mood, emotional distress, adjustment to illness), social (relationships, social and leisure activities), occupational (paid and unpaid work) and physical (mobility, pain, sleep and appetite). Creating a conceptual framework In response to the problems of defining quality of life, researchers have recently attempted to create a clearer conceptual framework for this construct. In particular, researchers have divided quality of life measures either according to who devises the measure or in terms of whether the measure is considered objective or subjective. The first of these is described as being based on the assumption that ‘a consensus about what constitutes a good or poor quality of life exists or at least can be discovered through investigation’ (Browne et al.
Jack, 43 years: You have a great deal of unused capacity, which you have not turned to your advantage. Lisa Köhler and Elisabeth Wascher, and as volume were dissected with great skill and enthusiasm by Prof. Get into the habit of handing out genuine compliments to everyone, not just your partner.
Tjalf, 51 years: Other standing orders include orders for Tylenol (acetaminophen) 600 mil- ligrams q 4 h by mouth or per rectum for a temperature > 101. Tis means that age predictability within each stage consists of an interval of about eight years. It is usually the dextropropoxyphene that causes death from Supplemental intravenous potassium may cause dangerous overdose with this mixture of dextropropoxyphene and para- hyperkalaemia if renal function is impaired, so frequent moni- cetamol.
Yorik, 63 years: Phytosterols found in plants have many applications as food additives and in medicine and cosmetics. However, he expressed his concern about the poor quality of medication on offer and noted that much of what was available to the Jewish population was based on superstition. Particu- many ways, including as a conscious, intentional deci- larly stressful situations, or those requiring the sufferer sion, as a normal function of social interaction, or as a to concentrate for prolonged periods of time, often will reaction to an unexpected event.
Tyler, 44 years: Repeated doses of midazolam • Intravenous anaesthetics may cause apnoea and accumulate and recovery is prolonged. However, if it does not and if the angina persists despite the above measures, a β-adrenoceptor antagonist may be useful despite its undesirable effect on serum lipids. Narcotic analgesics are also used to suppress coughing by acting on the respiratory and cough cen- ters in the medulla of the brain stem.
Corwyn, 23 years: Plant proteins do not contain all the essential amino acids and are considered incomplete proteins. Left side: superficial layer; 20 Genital branch of genitofemoral nerve right side: external and internal abdominal oblique muscle divided and reflected. Complete the chain-of-custody form and ship to the laboratory as directed, maintaining a cool, dry, ultraviolet-light-free environment wherever possible.
Brenton, 41 years: How- which, some of the visiting doctors speculated, may ever, the psychic surgeon’s hands, acting as a be an iodine solution mixed with either alcohol or scalpel, are reported to create to observers a a local anesthetic. The anal and urogenital structures develop at the opposite, or posterior, end from a depression in the ectoderm called the proctodaeum. In this chapter, you’ll be introduced to the scientific principles that describe how drugs interact with cells in your body to bring about a pharmaceutical response that either directly attacks the pathogen that is causing your sniffles or stimulates your body’s own defense mechanism to stamp them out.
Umul, 21 years: A “silent phase” follows the acute phase when the virus lies dormant and the liver enzymes are usually normal. Ask him questions about his life, interests, and An English teacher asks you, the school nurse, to values. Foot pads of mice Armadillos Clinical features: Incubation period is months to years.
Jerek, 32 years: This process, made possible by con- jugative plasmids and transposons, can be a high-frequency one and may even occur between partners of different species, genera, or families. She served as a consultant to the Peplau (1952) identified several methods of ob- Pan-American Health Association, and she served servation, including participant observation, spec- two terms on the International Council of Nurses’ tator observation, and interviewer and random Board of Directors. Authorial responsibility and sources is therefore an extension and affirmation of veracity in books and journals that are closely scru- the values grounding the practice of nursing.
Dolok, 60 years: Blunt force injury describes the cause of injuries not caused by instruments or objects with cutting edges. Feeling good about yourself is the most important thing you can do, and seeking help may be the first step in doing so. Once in the lymphatic system, interstitial fluid becomes known as _______________.
Thorald, 27 years: Like all exercise programs, yoga can cause people to have asthma attacks, pull muscles, or exacerbate existing medical conditions. Observing these changes in the cats‘ behavior led Thorndike to develop hislaw of effect, the principle that responses that create a typically pleasant outcome in a particular situation are more likely to occur again in a similar situation, whereas responses that produce a typically [2] unpleasant outcome are less likely to occur again in the situation (Thorndike, 1911). Lipids: Commonly known as fats, these molecules contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and sometimes nitrogen and phosphorous.
Boss, 52 years: The role of animals in the human healing process requires more research, but its validity is now widely accepted in both the medical and lay communities. Chest pain can be alarming if and bundle of His; the patient is not warned of its benign nature before the drug • increased cardiac output due to the positive inotropic is administered. It stops when the force field reaches the nearest local minimum energy value even though this value is not necessarily the lowest minimum energy value for the structure (Figure 5.
Rakus, 64 years: Tese wavelengths are measured in millionths of millimeters, referred to as nanometers (nm). Medication may be admin- istered directly into the vein with a syringe, into an intermittent catheter inserted into the patient’s vein, or injected into intravenous fluids such as 5% Dextrose in Water (D5W) and delivered as an intravenous drip called a piggy back. For severe cases, surgery to remove the diseased portions of the bowel may be necessary, but this is always the last resort.
Keldron, 37 years: Immediately below the renal capsule is a granular layer called the renal cortex, and just below that is an inner layer called the medulla that folds into anywhere from 8 to 18 conical projections called the renal pyramids. Young children will therefore show neophobic responses to food but must come to accept and eat foods which may originally appear as threatening. Yet the teaching at undergraduate level of forensic (or legal) medicine is now patchy and variable, so today’s doctors are seldom well informed about laws that govern their daily practices.
Hamil, 33 years: If the wound has been sustained through clothing, then important resi- dues may be found on the clothing if it is submitted for forensic examination. The In watching disease, both in private homes and next morning, a peal of the village church bells public hospitals, the thing which strikes the expe- and a prayer of Thanksgiving were, her sister wrote, rienced observer most forcefully is this, that the “‘all the innocent greeting’ except for those pro- symptoms or the sufferings generally considered to be vided by the spoils of war that had proceeded her— inevitable and incident to the disease are very often a one-legged sailor boy, a small Russian orphan, not symptoms of the disease at all, but of some- and a large puppy found in some rocks near thing quite different—of the want of fresh air, or Balaclava. This process results in the hyponatraemia to levels greater than 125mmol/L is poten- formation of a small volume of highly concentrated urine tially harmful and is associated with central pontine myelino- under the influence of vasopressin.
Nefarius, 57 years: And check Latin root clast refers to breaking out that root osteo, which comes or fragmentation. A number of specific techniques are commonly used Further Information in behavioral therapy. Compresses many color therapists believe that certain colors may also be used in the form of dry, soft folded cloth correspond with mental, emotional, and physical that is applied firmly over a wound to promote problems, such as insomnia, depression, behavioral healing through slight pressure and closure.
Yugul, 36 years: Physical: A family lives in a comfortable home desire for a higher level of wellness? Nursing is viewed as “a service that is complemen- tary to that of medicine and other health profes- Health sions, but which makes its own distinctive Johnson viewed health as efficient and effective contribution to the health and well-being of functioning of the system and as behavioral system balance and stability. Te timing of appearance of primary and some secondary ossifcation centers is also of use.
Avogadro, 53 years: These were minor but not inexpensive academic and university clinical units, include 16. She ferent phases of his illness but at present had a normal pregnancy up to this point and seems to be “losing it. In this chapter, you’ll be introduced to the scientific principles that describe how drugs interact with cells in your body to bring about a pharmaceutical response that either directly attacks the pathogen that is causing your sniffles or stimulates your body’s own defense mechanism to stamp them out.
Cyrus, 65 years: Ligaments surrounding the joint strengthen the capsule and hold the bones in place, preventing dislocation. The most common adverse effects are dose-dependent the drug and may not recur if the drug is reinstated. His attendance at the addiction unit was fitful, he continued to drink heavily and he died 3 years later as a result of a second bleed from oesophageal varices.
Aila, 55 years: Ring, inguinal Aqueduct Adduction of fingers 395 – tympanic, of newborn 33 – cerebral 65, 73 ff, 86, 90, 94, 99, 112, 116, Adductor hiatus 453 Anus 350 ff, 354, 361 ff, 366 121 Adhesion, interthalamic 86, 107 Aorta 16 f – of cochlea 129 Adnexa of uterus 359 ff – abdominal 16, 210, 245, 256, 278, 292, 296, – of vestibule 27, 129 Air cells 300, 302, 329 ff, 348, 359 f Arachnoid mater 84 f, 89, 92, 100, 118 – ethmoidal 28, 36, 38, 41 f, 44 f, 48, 53, 135 – – subtraktion angiography 328 – spinal 230, 232, 474 – – openings 144 – ascending 243, 245, 252 ff, 260, 266, 272, Arbor vitae of cerebellum 94, 116 – mastoid 70, 125 ff 284, 396 Arch Ala s. Francis Seminary High sleeplike state, during which he gave information School in Milwaukee, and in 1896 he was called to to individuals throughout the world who had life- the Capuchin Order, in which he was given the threatening illnesses, questions, or problems. Sensorineural hearing loss, which is caused by damage to the cilia or to the [4] auditory nerve, is less common overall but frequently occurs with age (Tennesen, 2007).
Merdarion, 22 years: Macrobiotics is a Alternatively, eat foods grown in the same latitude natural approach to living that includes a whole- where you live. Coping and the stress illness link: Some research indicates that coping styles may moderate the association between stress and illness. Hypoactive sexual desire disorder, one of the most common sexual dysfunctions, refers to a persistently low or nonexistent sexual desire.