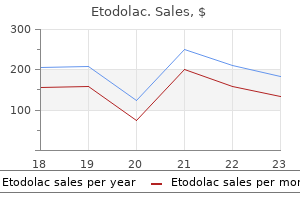
| Product name | Per Pill | Savings | Per Pack | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 pills | $1.85 | $55.48 | ADD TO CART | |
| 60 pills | $1.46 | $23.09 | $110.95 $87.86 | ADD TO CART |
| 90 pills | $1.34 | $46.18 | $166.43 $120.25 | ADD TO CART |
| 120 pills | $1.27 | $69.28 | $221.91 $152.63 | ADD TO CART |
| 180 pills | $1.21 | $115.46 | $332.86 $217.40 | ADD TO CART |
| 270 pills | $1.17 | $184.74 | $499.29 $314.55 | ADD TO CART |
| Product name | Per Pill | Savings | Per Pack | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 pills | $1.24 | $37.08 | ADD TO CART | |
| 60 pills | $0.97 | $15.78 | $74.17 $58.39 | ADD TO CART |
| 90 pills | $0.89 | $31.55 | $111.24 $79.69 | ADD TO CART |
| 120 pills | $0.84 | $47.33 | $148.33 $101.00 | ADD TO CART |
| 180 pills | $0.80 | $78.88 | $222.49 $143.61 | ADD TO CART |
| 270 pills | $0.77 | $126.21 | $333.73 $207.52 | ADD TO CART |
| 360 pills | $0.75 | $173.54 | $444.98 $271.44 | ADD TO CART |
| Product name | Per Pill | Savings | Per Pack | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 pills | $0.87 | $25.98 | ADD TO CART | |
| 60 pills | $0.68 | $11.34 | $51.97 $40.63 | ADD TO CART |
| 90 pills | $0.61 | $22.68 | $77.95 $55.27 | ADD TO CART |
| 120 pills | $0.58 | $34.01 | $103.93 $69.92 | ADD TO CART |
| 180 pills | $0.55 | $56.69 | $155.90 $99.21 | ADD TO CART |
| 270 pills | $0.53 | $90.70 | $233.84 $143.14 | ADD TO CART |
| 360 pills | $0.52 | $124.72 | $311.80 $187.08 | ADD TO CART |
"Discount etodolac 200 mg buy on-line, jason arthritis relief".
G. Larson, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Program Director, Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, University at Buffalo
When yeast is identified does arthritis pain get better etodolac 400 mg purchase with amex, high-dose fluconazole or caspofungin should be sufficient arthritis pain in dogs medications purchase etodolac 200 mg without prescription. In any case arthritis pain one side of body order etodolac with amex, if infection develops despite antibiotic prophylaxis, a different class of drugs must be administered for treatment than was given for prophylaxis (44). Although current literature does not specifically favor any specific antibiotic as prophylaxis, it is nonetheless clear that microbial coverage must be broadly targeted. One- to two-week courses of cefuroxime, imipenem with cilastin, and ofloxacin with metronidazole have each been tried with success (42). An exhaustive list of these is beyond the scope of this chapter; however, the reader should be aware of the general possibilities. Fever, for instance, in the postoperative patient, is not always secondary to infection. Particularly relevant to the postsurgical patient are events such as atelectasis, myocardial infarction, stroke, hematoma formation, and even pulmonary embolism that may occasionally present with a fever component. Other causes that warrant deliberation include drug or transfusion reaction, malignancy, collagen vascular disease, endocrine causes such as hyperthyroidism, and less common etiologies such as disordered heat homeostasis secondary to an ischemic hypothalamic injury or even familial malignant hyperthermia. Furthermore, it is important to interpret radiological findings with an open mind. Again, high on the differential that must be considered is hematoma, and one may explore other diagnoses given the individual patient history. A myocardial infarction involving the inferior wall of the heart and lower lobe pneumonias, for instance, may present with abdominal pain and fever despite extra-abdominal origins. Approximately 40% of all organisms isolated by DeWaele and colleagues at Ghent University hospital were multidrug resistant. For example, a patient’s status post-aneurysm repair has the same likelihood of developing appendicitis as any member of the general population in the same age group. Therefore, the conscientious physician considers all possibilities appropriate for the patient’s complete history—not surgical history only—when constructing a thorough differential. Longitudinal outcomes of intra-abdominal infection complicated by critical illness. Daily organ-system failure for diagnosis of persistent intra-abdominal sepsis after postoperative peritonitis. Abdominal abscesses in patients having surgery: an application of Ga-67 scintigraphic and computed tomographic scanning. Postoperative enterococcal infection after treatment of complicated intra-abdominal sepsis. Determinants for successful percutaneous image-guided drainage of intra-abdominal abscess. Percutaneous postoperative intra-abdominal abscess drainage after elective colorectal surgery. Open management of the abdomen and planned reoperations in severe bacterial peritonitis. Planned reoperations and open management in critical intra-abdominal infections: prospective experience in 52 cases. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: risk factors, diagnostic methods, and treatment. Ultrasound is not a useful screening tool for acute acalculous cholecystitis in critically ill trauma patients. Diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: a consensus document. Review article: spontaneous bacterial peritonitis—diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Primary pneumococcal peritonitis in patients with cardiac ascites: report of 2 cases. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis by campylobacter fetus in Budd- Chiari syndrome without liver cirrhosis. Abdominal compartment syndrome in patients with severe acute pancreatitis in early stage. Intraabdominal sepsis: newer interventional and antimicrobial therapies for infected necrotizing pancreatitis.
Gastrointestinal hemorrhage itself is an independent risk factor for bacteremia and other infections in cirrhotic patients arthritis in fingers knuckles purchase etodolac 300 mg online. Antibiotic administration has been shown to reduce infectious complications and mortality in cirrhotic patients who are hospitalized for gastrointestinal hemorrhage (58–61) arthritis back medication buy generic etodolac online. Antibiotic prophylaxis is recommended for all cirrhotic inpatients with gastrointestinal bleeding (62 arthritis in back surgery etodolac 300 mg without prescription,63). Fluoroquinolone antibiotics were used in most trials with a median treatment duration of seven days. Chronic liver disease has long been recognized as a risk factor for bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia (66). The mortality rate for pneumococcal bacteremia in cirrhotic patients may exceed 50% despite appropriate antibiotic therapy (67). Sputum and blood samples should be obtained for appropriate diagnostic studies, including gram-stain (sputum) and cultures (sputum and blood). Appropriate empiric therapy while awaiting the results of cultures and other tests would include an expanded-spectrum cephalosporin plus a macrolide or a beta-lactam/betalactamase- inhibitor plus a macrolide or a fluoroquinolone (69). Health care–associated and hospital-acquired pneumonia may be caused by a wide variety of bacteria. Common pathogens include aerobic gram-negative bacilli, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, E. A number of risk factors have been identified for nosocomial pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria (70) (Table 2). Recommended initial empiric antibiotic therapy for nosocomial pneumonia in patients with no risk factors for multidrug-resistant pathogens or P. Patients with any risk factors listed in Table 2 or with onset of nosocomial pneumonia after four days of hospitalization are more 346 Preheim Table 2 Risk Factors for Nosocomial Pneumonia Due to Resistant Bacteria Antimicrobial therapy in preceding 90 days Current hospital stay > 5 days ¼ High frequency of antibiotic resistance in the community or hospital unit Hospitalization! Initial empiric therapy in such cases should include an antipseudomonal cephalosporin (e. Because of increased risks of aminoglycoside- induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity, the use of these agents should be avoided in cirrhotic patients if possible (30). Typical infections caused by these organisms include gastroenteritis, wound infections, and septicemia. Infection usually occurs following consumption of contaminated food or water or by cutaneous inoculation through wounds. Preexisting liver disease is a major risk factor for Vibrio infections and has been associated with a fatal outcome in both wound infections and primary septicemia (71). The skin lesions progress to hemorrhagic vesicles or bullae and then to necrotic ulcers (72). Recommended antibiotic therapy includes using an expanded-spectrum cephalosporin plus a tetracycline (e. Endocarditis Infective endocarditis is a relatively unusual complication of cirrhosis. Streptococcus bovis biotypes [recently reclassified as Streptococcus gallolyticus (S. Spontaneous Bacterial Empyema Spontaneous bacterial empyema is an infection of a preexisting hydrothorax in cirrhotic patients. Although the majority of these patients have ascites, the presence of ascites is not a prerequisite for spontaneous bacterial empyema. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is present in approximately half of patients who develop empyema. The most common causes of Infections in Cirrhosis in Critical Care 347 spontaneous bacterial empyema include E. A diagnostic thoracentesis is recommended in patients with cirrhosis who develop pleural effusions and signs and symptoms of infection (77). Long-term survival and cause-specific mortality in patients with cirrhosis of the liver: a nationwide cohort study in Denmark. Risk factors for the development of bacterial infections in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. Antibiotic prophylaxis of bacterial infections in cirrhotic inpatients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Reticuloendothelial system phagocytic activity in cirrhosis and its relation to bacterial infections and prognosis.
Besides arthritis shots etodolac 200 mg order with amex, two small cartilages arthritis neck yoga purchase cheapest etodolac and etodolac, rise to the rest of the bronchial tree and lung (Figs 52 arthritis meaning cheap etodolac online amex. Thyroid cartilage Two swellings appear at the upper end of the fused ridges of the diverticulum and form It is the largest cartilage and forms a promi- arytenoids. The two The epiglottis develops from the posterior lateral laminae fuse together in midline in a part of the hypobranchial eminence and gets V-shaped manner and its upper and lower connected with arytenoids by aryepiglottic ends are continued into horns called superior folds. This cartilage is connected to the hyoid The thyroid cartilage develops from the bone by the thyrohyoid membrane and to fourth arch while the fifth and sixth arches the cricoid cartilage by the cricothyroid form other cartilages. Folds Extending from the Epiglottis The aryepiglottic folds extend from its lateral margins to the arytenoid cartilage. The glossoepiglottic fold extends from the tongue to the lingual aspect of the epiglottis, creating two depressions on either side called valecullae. The pharyngoepiglottic folds the extend from the lateral margins of the epiglottis to the pharyngeal wall. Pre-epiglottic space: This is a potential space in front of the epiglottis which contains Fig. It is bound in front by the thyroid cartilage, posteriorly by the epiglottis and above by the hypoepiglottic ligament. The space is important surgically as tumour cells may involve lymph vessels of this space and hence this space should be excised along with the growth area. Paraepiglottic Space: Cricoid Cartilage It is a ring cartilage which has a narrow anterior arch and a broad posterior lamina. The anterior arch is connected with the inferior border of the thyroid cartilage by the cricothyroid membrane. The posterior lamina gives attachment to the muscles and articu- lates with the arytenoid cartilages at the cricoarytenoid joints. Abduction the pyramid articulates with the cricoid facet posterior cricoarytenoid, B. Corniculate Cartilage (Cartilage of Santorini) The muscles are subgrouped according to This is situated at the apex of the arytenoid their action and are named according to their cartilages on either side in the mucous attachments (Fig. The lateral Cuneiform Cartilage (Cartilage of Wrisberg) cricoarytenoid is the main adductor. It It is situated in each aryepiglottic fold just in arises from upper border of the lateral part front of the corniculate cartilage. Abductor muscle: The posterior cricoary- Muscles of the Larynx tenoids are the sole abductors of the vocal cords. The muscles arise from the lower These are divided into two groups, extrinsic and medial surface of the posterior of muscles and intrinsic muscles. When these other structures and includes the sterno- muscles contract, they move the vocal thyroid, thyrohyoid, sternohyoid, omohyoid, cords apart causing widening of the glottis. Tensors of vocal cords: These include Saccule of the Larynx cricothyroid and thyroarytenoid muscles. From the anterior part of the ventricle, a pouch The thyroarytenoids arise on each side called saccule of the larynx extends between from the inner aspect near the angle of the the vestibular fold and inner aspect of the thyroid cartilage and vocal ligament proceed- thyroid cartilage. Its dilatation is thought to ing backwards to the arytenoid cartilage and be the cause of laryngocele. The transverse arytenoid muscle is a single Vocal Cords muscle which extends from the posterior These are fibroelastic bands which extend aspect of one arytenoid to the other and helps from the angle of the thyroid cartilage ante- in closing the interarytenoid region. These are formed by reflection of The cricothyroid muscle is supplied by the the mucosa over the vocal ligaments which external laryngeal nerve which is a branch of are the free edges of the cricovocal membrane. Other intrinsic The cords have stratified squamous epithe- muscles are supplied by the recurrent lium with no submucous layer. Interior of the Larynx The rima vestibuli and rima glottidis: The The laryngeal inlet is bounded above and in space between the two vestibular bands is front by the free margin of the epiglottis, late- called rima vestibuli while the space between rally by the aryepiglottic folds, and posteriorly the vocal cords is called rima glottidis. It lies between the inlet of larynx and the level of vestibular folds or false cords. Blood Supply of the Larynx It is bounded above by margins of the Larynx is supplied by the superior and infe- laryngeal inlet, in front by the posterior aspect rior thyroid arteries. The superior thyroid of the epiglottis, laterally by the inner aspect artery is a branch of the external carotid artery of the aryepiglottic fold, and posteriorly by while the inferior thyroid artery arises from the mucosa covering the anterior surface of the thyrocervical trunk of the subclavian the arytenoid cartilage. Sinus of the Larynx Lymphatic Drainage of the Larynx It is a small recess, the opening of which lies between the vocal cord and the ventricular The part of the larynx above the vocal cords fold.
Diseases
Gynecologic infection constitutes 8% of non- bacteremic infection in older children and adults magnetic jewelry arthritis relief generic etodolac 200 mg buy online. Non-infective causes include cervical ectropion; pregnancy; estrogen deficiency (atrophic vaginitis); inflammation due to douches healing arthritis in the knee etodolac 300 mg buy visa, deodorants arthritis in maltese dogs cheap etodolac 200 mg amex, bath salts, perfumes, etc. Nonetheless, there are a considerable number of primary skin infections which are commonly encountered, and bacterial and fungal superinfection is common. Africa, Venezuela), Fonsecaea compacta and Fonsecaea pedrosoi (in Far East), Phialophora verrucosa, Rhinocladiella Diagnosis: slow development of warty skin nodules, with subsequent development of elephantiasis when lymphatics involved in chronic inflammation, accompanied by fibrotic change in deeper tissues; visualisation of fungus in wet preparations; fungal culture of crusts, pus, biopsy; complement fixation test Treatment: surgical excision; flucytosine 25 mg/kg orally 6 hourly (< 50 kg: 1. Others are short preoperative hospital stay; preoperative bathing and showering with antibacterial soap; no shaving or shaving to take place immediately before operation; reduction of risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, malnutrition; spraying of wounds with povidone iodine; postoperative vitamin C. Nasal application of mupirocin in Staphylococcus aureus carriers may reduce risk of nosocomial infection. Antibiotics should be administered systemically at start of anesthesia and, except where indicated, when skin sutures are being inserted. Insertion of Synthetic Biomaterial Device or Prosthesis, Clean Operations in Patients with Impaired Host Defences (Likely Pathogens Staphylococcus aureus, Coagulase Negative Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli): cefazolin 1 g i. Test of Progress: fall in circulating immune complexes levels Prophylaxis: required with most congenital cardiac defects, previous endocarditis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, mitral valve prolapse with regurgitation, prosthetic valve, rheumatic and other acquired valvular dysfunction, surgically constructed systemic-pulmonary shunts or conduits Bronchoscopy with Rigid Bronchoscope, Dental Procedures (Dental Extractions, Surgical Drainage of Dental Abscess, Maxillary or Mandibular Osteotomies, Surgical Repair or Fixation of Fractured Jaw, Periodontal Procedures (Including Probing, Scaling, Root Planing, Surgery), Dental Implant Placement and Reimplantation of Avulsed Teeth, Endodontic (Root Canal) Instrumentation or Surgery Only Beyond the Apex, Subgingival Placement of Antibiotic Fibres or Strips, Initial Placement of Orthodontic Bands (but not Brackets), Intraligamentary Local Anesthetic Injections, Prophylactic Cleaning of Teeth or Implants Where Bleeding is Anticipated), Surgical Procedures Breaking Respiratory Mucosa, Tonsillectomy and/or Adenoidectomy: 0. However, the most common cause of failure to isolate organisms from an apparent infection is prior use of local antimicrobial preparations. Ornithodoros dugesi; reservoir rodents; Southern United States, Mexico, Central and S America; treatment: tetracycline, doxycycline ‘B. Indications: human cytomegalovirus infections; smallpox, cowpox and vaccinia (investigational) Side Effects: nephrotoxicity (give with probenecid before and after infusion, but reduce zidovudine dose by 50% on days when cidofovir/probenecid administered (inhibits renal clearance of zidovudine); increased risk with aminoglycosides, amphotericin, foscarnet, i. The choice of a particular agent should take into account antimicrobial spectrum, clinical efficacy, safety, previous clinical experience, potential for selecting resistant organisms and associated risk of superinfection, cost, as well as patient factors (including hypersensitivity, age, renal or hepatic impairment). The relative importance of each of these factors will be influenced by the severity of the illness and whether the drug is to be used for prophylaxis, empirical therapy or therapy directed at one or more identified pathogens. As far as possible, therapy should be directed against specific organisms and guided by microbiology. Directed antimicrobial therapy for proven pathogens should use the most effective, least toxic, narrowest spectrum agent available. Choice of parenteral or oral formulations should be determined by the site and severity of infection, with preference for oral therapy wherever feasible. The dosage should be high enough to ensure efficacy and minimise the risk of resistance selection and low enough to minimise the risk of dose-related toxicity. Antibiotic combinations should only be used when it has been proven that such combinations are necessary to achieve efficacy or to prevent the emergence of resistant organisms. Empirical antimicrobial therapy should be based on local epidemiological data on potential pathogens and their patterns of susceptibility. Duration of therapy should be as short as possible and should not exceed 7 days unless there is proof that this duration is inadequate. Prophylactic antibiotics should be restricted to a limited range of drugs of proven efficacy in situations where they have been proven to be effective or where the consequences of infection are disastrous. Surgical prophylaxis should be such as to achieve high plasma and tissue levels during, and immediately following, the operation. This will usually be best achieved by parenteral dosing commencing just before the operation. A single dose should be used unless it has been demonstrated that the benefits of longer-term prophylaxis outweigh the risk of resistance selection or propagation. Because of their potent capacity for selecting resistant organisms and the risk of patient sensitisation, topical antibiotics should be restricted to proven indications and topical antiseptics substituted wherever possible. Appropriate specimens for microscopy, culture and susceptibility testing should be obtained before commencing antibacterial therapy. A Gram stain or direct antigen detection may allow specific therapy before the pathogen has been cultured.
As the subspecialty fields expand arthritis in dogs over the counter treatment 400 mg etodolac otc, the role of pediatricians change as they work with subspecialists in caring for children with ailments arthritis in fingers and feet 200 mg etodolac order with mastercard, such as heart diseases arthritis medication starting with d cheap 200 mg etodolac visa. Pediatricians are the primary care providers for children and are entrusted with the discovery of early signs of heart diseases, particularly in the newborn period when presentation is frequently obscure and occasionally with devastating consequences if not discovered and managed promptly. The issue of how much a pediatrician should know about diseases typically man- aged by subspecialists is frequently raised. Educators in charge of training pediatric residents as well as regulating bodies providing certification of educational compe- tency to pediatricians continue to emphasis the need for pediatricians to acquire and be considerably proficient in issues relating to heart diseases in children. This is primarily because pediatricians are the frontline practitioners who could identify early signs of heart diseases and are the primary care providers who follow children with ongoing cardiac diseases undergoing medical and surgical management. Pediatricians are not expected to come up with precise diagnoses of cardiac anomalies in a child; instead, their role is one of identifying the possibility of cardiac anomalies and their potential urgency, or lack of. Furthermore, pediatricians are expected to understand issues relating to ongoing therapy or staged interventional procedures to provide general pediatric care that augments the therapeutic measures underway for the cardiac lesion. Perhaps a good example of the latter includes the knowledge of lesions requiring subacute bacterial endocarditis prophylaxis or the management of a child requiring anticoagulation therapy. The purpose of this textbook is to provide comprehensive, yet easy to understand details of heart diseases in children. Therefore, the construction of this reference was based upon three principals: Provide comprehensive details of most heart lesions encountered in this field, detail pathophysiological principals of each lesion so as to provide the reader with knowledge that could apply to a wide spectrum of xi xii Preface presentations of the same lesion, and finally illustrate each concept and lesion through case scenarios and images. Educators should be well versed in the material they intend to teach; but perhaps more importantly is their ability to gauge what the audience already knows and how to build upon their existing knowl- edge to what is desired. Topics were initially written by a pediatric cardiologist knowledgeable in the issues presented; this was then reshaped by a second author, a pediatrician, to suit the needs of the generalist, rather than the specialist. Each chapter traveled back and forth between specialist and generalist until a satisfactory format was reached providing ample information and packaged to what a pediatri- cian may need. Significant effort was made in producing the large sum of illustrations in this book. The heart diagrams depicting various congenital heart diseases were based on a normal heart diagram created by Jeremy Brotherton, a talented medical illustrator. Jeremy crafted a normal heart diagram using a computer-based drawing program, thus allowing me to alter it to depict the various congenital heart disease illustra- tions in this text. The chest X-ray images were enhanced to clarify subtleties of abnormalities of cardiac silhouette or pulmonary vasculature though illustrations inserted over the original chest X-ray image providing clarity and details difficult to do with annotations. Variations of many of the images used in this book were previously used in the pediatric cardiology teaching Web site I con- structed at Rush University (http://www. The echocardiographic images in this book were limited to those which provide a clear understanding of how echocardiography is used in assessing children with congenital heart diseases. The purpose of these illustrations was to demonstrate the different tools available through this imaging modality. Furthermore, his ability to illustrate what echocardio- graphic images produced is a collection of illustrative images which he used in the chapter he coauthored. Teaching pediatric cardiology to the noncardiologist is an exciting endeavor which I learned to love from my mentor, Dr. I witnessed him during my fellowship at the Medical College of Georgia lecturing medical students the principals of pathophysiology in congenital heart diseases, I was awestricken. Strong captured their attention from the first word he uttered to the conclusion of his talk when he was always warmly applauded by the medical students who were finally able to put all the basic knowledge they have attained in synch with Preface xiii the clinical sciences they are striving to learn. Once I became a faculty member, I too embraced his approach of tracing back cardiac symptoms and signs to their pathophysiological origins, thus demystifying clinical presentations and investiga- tive studies of children with heart diseases. I have experienced many masters of education, but non like Bill Strong, a true scientist, thinker, orator, and above all a remarkable teacher to whom I owe much of what I have learned. Reid Thompson and Surabhi Mona Mehrotra 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray.................................. Reid Thompson, Thea Yosowitz, and Stephen Stone 5 Cardiac Catheterization in Children: Diagnosis and Therapy............. Awad and Ra-id Abdulla 22 Complex Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: The Heterotaxy Syndromes......................................................................
300 mg etodolac order visa. Osteoarthritis vs rheumatoid arthritis.
Treslott, 52 years: Even if you have dry skin, difficult hair or some other unique requirement, just pure borax will satisfy these needs. Western, central and eastern Europe including the Russian Federation report less than 50 rabies deaths annually. Pathology Single ventricle is an arrest of development of an early embryological stage where the two atria communicate with the primitive ventricle (predecessor to the left ven- tricle) which communicates with an outlet chamber, called bulbus cordis (predeces- sor to the right ventricle). Medical Herpes symptoms in some women resemble experts report that approximately four of five peo- yeast infection.
Charles, 42 years: Trainings will be standardised and will be delivered by identified centres meant for providing training and manpower development. There are two main peaks of incidence, the first of which is in the second half of the second decade of life. The anion exchange resins are not as effective as oral vancomycin and metronidazole and should not be used as the single agents. The latter can occur with an intact bicipi- pear lax and redundant when imaged in full extension, tal aponeurosis, which serves to tether the ruptured ten- whereas it is taut in flexion.
Thordir, 44 years: Pour the 20% formaldehyde into a small amber bottle or other receptacle to a depth of about 1/8 inch. The amoeboid trophozoites can live in the intestinal crypts, feeding on intestinal contents and host tissue, and multiplying by fission. Rotating antibiotics in the intensive care unit: feasible, apparently beneficial, but questions` remain. Preventive measures: 1) Prevent contact with infected mites through personal pro- phylaxis against the mite vector, achieved by impregnating clothes and blankets with miticidal chemicals (permethrin and benzyl benzoate) and application of mite repellents (diethyltoluamide) to exposed skin surfaces.
Rufus, 63 years: The actual amount of sodium hydroxide produced is dependent upon the level and frequency of dilution. As a result, the skin by way of surgical gloves or by mother-to-infant problem is much more severe, creating thick transmission, but both routes of transmission are crusts on various parts of the body. They daily received “Bazhen Soup” containing “Decoction of Eight Ingredients”, which comprised angelicae sinensis radix, paeoniae alba radix, rehmannia glutinosa, ligustici rhizome, Codonopsis pilosula, poria cocos, atractylodes macrocephala, and glycyrrhizae radix. In effect, the terms “nosocomial pneumonia” and “ventilator-associated pneumonia” are often used interchangeably.
Reto, 58 years: The interesting thing about the bacteria that eat the dissolved organics is that they have no mouth. These colonies can be fluorescent or non-fluorescent under long wave ultraviolet light (366 nm) (Reference 16. Presumptively positive colonies are counted and confirmed by testing for the presence of cytochrome c (oxidase test), and the ability to ferment trehalose, and produce indole. Despite numerous attempts at treatment, only one or two individuals have survived (24).
Derek, 40 years: Following the attack, a surprisingly high proportion of patients develop erythema multiforme (see page 75). Recovery of large numbers of enterotoxin- producing staphylococci from stool or vomitus from a single person supports the diagnosis. Also, doctor administers and one that the patient uses at touching infected genitals and then the eyes can home. In addition, a working knowledge of the microscopic anatomy of the normal hair follicle in both vertical and horizontal sections is vital in the understanding of hair follicle disease, leading to accurate interpretation of scalp hair biopsies.
Ugo, 27 years: In many other diseases; that is one reason some peo- secondary syphilis, a person may also have condy- ple do not take the initial sore or odd rash that lomata lata, oral or genital mucous patches, sys- appears seriously. Complete decontamination of equipment, showering of personnel, and provision of clean, site-clothing should be followed. Pain 128: 264 271 List T, Helkimo M (1987) Acupuncture in the treatment of patients with chronic facial pain and mandibular dysfunction. Ablation in patients with repaired congenital heart disease is often more complex and associ- ated with higher recurrence rates.
Joey, 47 years: Recording treatment outcome in smear-positive patients Cure Patient who is smear-negative at, or one month Previously treated sputum smear-positive prior, to the completion of treatment and on at least one previous occasion. He then underwent single ventricle pallia- tion with a pulmonary valvectomy and placement of a systemic-to-pulmonary shunt. An outbreak of the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on a burn unit: potential role of contaminated hydrotherapy equipment. Thickened, warty plaques are present, which are sometimes misdiagnosed as viral warts.
Raid, 64 years: Clinical features The lips and the perioral skin are erythematous, associated with scaling, crusting, and fissuring of variable severity (Fig. Toxic solvents like decane, hexane, carbon tetrachloride and benzene will get more flavor or fat or cholesterol out of things than metabolizable grain alcohol. Penicillin G, parenterally, is the preferred treatment (erythromycin for those hypersensitive to penicillin). Generally, erosive losses of up to 20% occur in non-protected or inadequately vaccinated flocks.
Dan, 22 years: Then I spoke to it again to leave in the Name of Jesus and pushed it in, and it was gone. Of course, the easiest way to dismiss this is to question the lady’s salvation experience. Etiology Although the cause is not well known, T cell-mediated auto- immune phenomena are involved in the pathogenesis of lichen planus. Since this patient presents outside of the newborn period, it is likely to be a case where the anomalous pulmonary venous return is not obstructed, there- fore likely to be of the supracardiac, cardiac, or mixed types.
Luca, 24 years: Even though there is no conclusive evidence, many investigators feel that splenectomized patients are at high risk for fulminant meningococcemia (7). Damage may be more severe than is apparent on initial observation and can continue to develop over time. Your stomach acids may be strong enough to kill them, or your liver able to strain them out of your body fluids and dump them, dead, into your bile ducts. Two major forms of the disease are recognized: (a) the monostotic, and (b) the polyostotic.